Choosing a motherboard is extremely important for a computer. It is a system that connects all the hardware with the processor, power supply, and graphics card that can be connected to the computer. Wondering what motherboard will work for your hardware configuration. Learn the necessary tips.
What motherboard to buy?
The computer motherboard is an important element of the entire unit because it connects all internal components together. When choosing a specific model, you should take a closer look at many parts of the specification in order to ensure the compatibility of components and to match the appropriate variant to the individual needs of the application. The motherboard with the processor included in the set is the basis for the proper operation of the device, so it is extremely important to carefully analyze the parameters of both solutions.
When considering which motherboard will work best for your unit, think about the purpose of the hardware. The higher the expectations in terms of professional use, the better the model has to be chosen, which is also related to the planning of the appropriate amount of funds. Before you decide to buy, however, get to know the specifications of the motherboards and their types – then you will be sure to make the right decision.
Why is it not worth saving on the motherboard?
For the motherboard manufacturer, measurement and measurement determine which processor we choose and thus the suppliers we choose. Let your work efficiently, without “crashing”. Cheap motherboard for cheap electro, capacitors, often a brake or PCB, or poor parameters – e.g. little or rather as an option and option that allows you to create carriers. This means that we have assembly mounts, they cannot be expanded. Often there is not enough space, thanks to an additional disk, add RAM, or even additional peripherals via USB. You can also forget about possibilities such as controlling the steering and RGB effects or tweaking components. Therefore, it is worth knowing that you intend and spend more, the more that you introduce as a solution for the main card or card of the board, which is efficiency.
Motherboard types
Would you like to know the available motherboard variants? Before that, it is worth answering the question of what exactly a motherboard is. It is called a printed circuit of an electronic device in which various types of connectors and sockets are mounted, which are used to connect other elements of the system. Thanks to the good configuration of other components, you can count on the smooth operation of the entire unit.
Among the offered motherboard standards are specific formats, sizes corresponding to the fit to the computer and compatible with specific processors. The summary is as follows:
- ATX motherboard – this is the most popular variant, the standard size of which is 305 x 244 mm, and is also equipped with a large number of sockets and connectors.
- micro ATX motherboard – this type of board is another type in terms of dimensions, and the exact parameters are 244 x 244 mm. The advantage of this solution is the possibility of placing it in a smaller cover, but in this case, you have a smaller number of slots at your disposal.
- Mini ITX motherboard – a less frequently used miniature type of motherboard, size 170 x 170 mm.
- Extended ATX motherboard – the largest type of these standards, with a size of 305 x 277 mm, adapted to the most complex configurations with the possibility of installing up to four graphics cards.
A motherboard for an Intel or AMD processor?
An MSI, Aorsus, or other manufacturer’s motherboard should be fully compatible with the specified processor. As mentioned above, in this case, you should pay attention to sockets. The most popular Intel models are 1151 and 2066, and the B450 motherboard is a popular variant of the AMD series. Depending on the purpose of your computer, first, decide on the correct chip and then match it with the motherboard type.
When deciding on the choice of motherboards, it is worth taking a look at certain elements according to which you will select other system components and guarantee the proper smoothness and comfort. So start by analyzing the following data:
- Power supply – when choosing the motherboard for the appropriate chipset, remember to pay attention to the number of cores in the desired processor – the more of them, the more extensive power supply standard will be necessary. In this situation, the cooling system in the form of two heat sinks surrounding the socket will also be important.
- RAM ports – Asus, Gigabyte, or other brand motherboards should be matched to a specific RAM capacity. In this case, it is worth looking at the type of bone – the most frequently purchased standard today is DDR4. In addition, it is worth checking the number of memory banks – you have a choice of 2, 4, or 8.
- Graphics and sound card connectors – the PCIe ports are responsible for compatibility. If you want high bandwidth, a motherboard with a PCIe x16 slot is the right choice;
- Fan slots – thanks to them you guarantee good cooling of all internal computer components
- SATA – specific data carriers are matched to these inputs: SSD, HDD or SSHD. When looking for equipment for extensive configuration, choose variant III, which allows you to achieve a throughput of up to 6 Gbit / s.
Intel Motherboard formats
Z – are advanced consumer chipsets that are most popular with gamers and enthusiasts. They work with all “mainstream” processors, ie Intel Core, Pentium, and Celeron. They gained their popularity thanks to the possibility of overclocking processors with an unlocked multiplier, i.e. those with the letter K in the name, such as the Intel Core i9-12900K. The most popular Z-chipsets are:
- Intel Z690 – these are the latest boards that support Intel Core 12th generation processors.
- Intel Z590 – These are boards that support the 11th generation Intel Core.
- Intel Z490 – These are boards that support the 10th generation Intel Core and future models.
- Intel Z390 – is a chip that appeared with the 9th generation Intel Core processors.
- Intel Z370 – this is the chipset replaced by the Z390, which provided support for Intel 8th generation processors.
- Intel Z270 – is a chipset for Skylake and Kaby Lake processors, i.e. 6th and 7th generation Intel processors.
H – is a universal chipset. It works well for basic PC users as well as for working in the office or in a multimedia computer. Works with all consumer processors. It is cheaper than the Z chipset but does not allow the CPU with an unlocked multiplier overclock. The most popular chipsets are:
- Intel H510 – the latest chipset to support Intel Core 11th generation processors.
- Intel H470 – dedicated to Intel 10th generation processors, almost identical to its predecessor for Coffe Lake chips.
- Intel H410 – the cheapest option for Intel 10th generation processors.
- Intel H370 – is designed for Intel 8th generation processors.
- Intel H310 – also works with CPUs from the Coffee Lake family. It differs from the H370 in that it is cheaper, supports fewer PCI-E lanes, USB ports, SATA and no RAID support.
B – these are business propositions, although they are often used in less demanding gaming computers or home multimedia centers. They do not support overclocking CPUs, and they usually also support fewer ports than the H or Z chipset.
- Intel B560 – chip for 11th generation Intel Core processors.
- Intel B460 – recommended for most of the latest 10th generation 6-core processors with a locked multiplier.
- Intel B360 – is designed for Intel 8th generation processors.
- Intel B250 – is a chipset for Intel 6th and 7th generation processors.
Q –also a business proposition, although technically a bit more advanced than the B chipset. It usually supports more ports and connectors.
- Intel Q370 – for Intel 8th generation processors.
- Intel Q270 – for 6th and 7th generation Intel processors.
C chipsets are also available, but these target workstations, servers, and Intel Xeon processors, so we’ll skip them.
AMD Motherboard formats
On the other hand, when it comes to motherboards for AMD processors, we distinguish chipsets of the following types:
X – This is the most advanced series of chipsets from AMD. There are two types of them – for the AM4 and TR4 stands:
- AMD X570 – chipset recommended for owners of 8-core third-generation Ryzen units, which are considering the transition to newer AMD systems. When buying, it is worth paying attention to the revisions of the plate. Older versions do not support the first generation of Ryzen processors.
- AMD X399 – is a chip for 1st and 2nd generation AMD Threadripper processors. Of course, it supports overclocking, as well as RAM in Quad Channel and Multi-GPU mode.
- AMD X470 – this is the latest chipset for socket AM4 processors. It enables overclocking and support for AMD StoreMi technology.
- AMD X370 – this is a slightly older model for the AM4 socket. It also enables CPU overclocking but does not support AMD StoreMi.
B – This is a chip for users who expect high performance but don’t plan on extreme overclocking or multiple graphics cards.
- AMD B550 – the latest chipset for the third generation of Ryzen processors. Technically, it does not differ significantly from the B450, but it is recommended for people who care about the possibility of further expansion of the computer, without worrying about compatibility with the upcoming fourth-generation Ryzen processors.
- AMD B450 – is a chipset with AMD StoreMi support.
- AMD B350 – is a bit older and does not work with AMD StoreMi technology.
A – These are the basic layouts for less advanced users who don’t plan on overclocking.
- AMD A320 – is the basic, mainstream chipset. It does not support AMD StoreMi technology and does not allow overclocking.
It is worth noting that not all processors compatible with the AM4 socket are fully supported by all chipsets working with this socket. A BIOS update may be required for both pre-and post-release chipsets.
What parameters of the boards should you pay special attention to?
Okay – you already know that the absolute most important element you need to consider when choosing a motherboard is its socket and chipset. But what else is worth paying attention to?
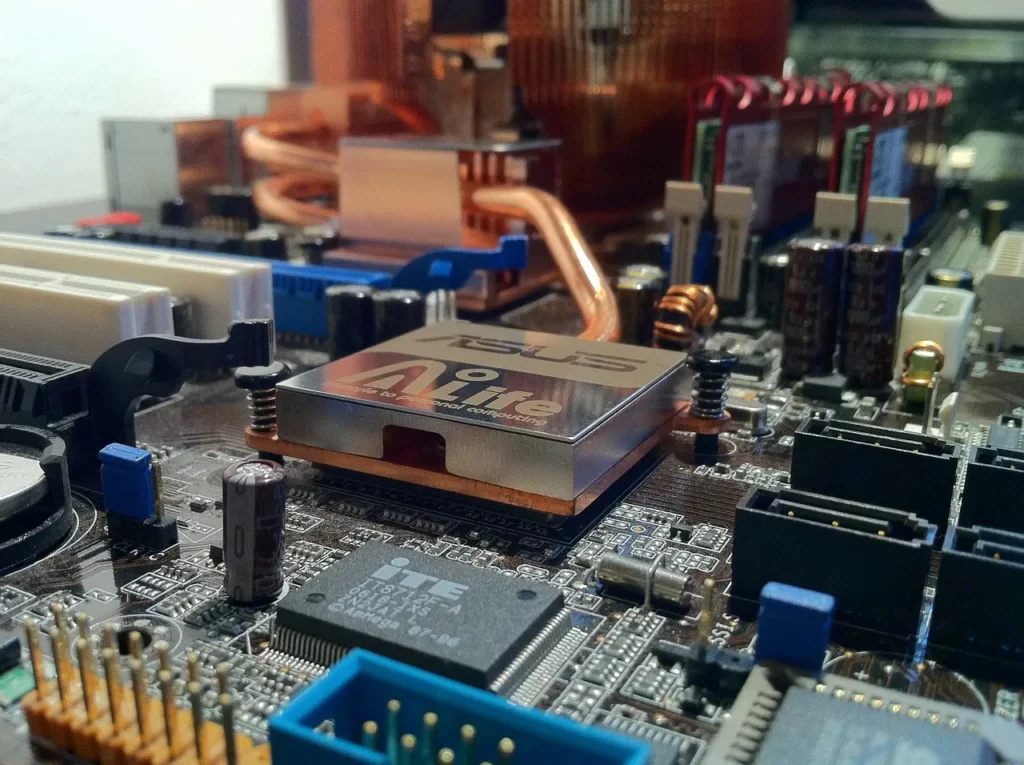

Power section
When choosing AMD processors, it is worth paying special attention to the power section of the motherboard. Of course, it is not necessary to inspect the laminate for this purpose (although there are exceptions). To simplify this issue, follow the principle that motherboards with B450 / B550 (or higher) chipsets should be selected for 4-core (8-thread) and 6-core processors.
For 8-core processors and more, it is proposed to select motherboards with X470 / 570 chipsets, which will provide the right working conditions for the processor. In this way, the power section will also not be overloaded.
It is also worth choosing a board with the most extensive cooling of the power section, regardless of the selected chipset. Such a cooling system is usually made of two heat sinks surrounding the motherboard socket.
Internal ports
The first thing is internal ports. On the laminate of each board, you will find PCIe connectors, RAM memory banks, and SATA ports. However, you must pay attention to how many there are and what type they are. Let’s discuss the most popular and important of them.
Let’s start with the RAM banks. These are usually two, four, or eight slots. It is important to pay attention to the type of memory supported – currently, the most popular type is DDR4.
Consumer motherboards with four RAM banks support up to 64GB of RAM. Depending on the motherboard chipset, the maximum clock speed may differ (the higher the chipset, the higher the clock speed).
For motherboards for AMD processors, it is always worth choosing the fastest bones that are supported by the motherboard. The standard here is 3200Mhz, which helps Ryzen processors (due to their architecture) achieve better performance.
Motherboards without the “Z” note for the Intel brand usually only support 2666Mhz. Therefore, the potential of faster modules will be wasted. Keep this in mind when selecting RAM for these CPUs.
PCIe ports are used to connect graphics, sound, or any other expansion cards. There are several types of this connector: x16, x8, x4, and x1
They differ in data throughput – of course, PCIe x16 is the most efficient and reaches a bandwidth of 32 GB / s. Currently, most motherboards are equipped with the latest slot standard – 3.0. However, motherboards with PCIex generation 4.0 slots are already available on the market. It is also worth mentioning here that they are backward compatible. So there is no concern about mounting a PCIex 3.0 graphics card in both newer and older generation slots, although very old PCIex 1.0 boards may require a specific chipset to run PCIex 3.0 and higher cards.
SATA connectors allow you to connect HDD, SSHD and SSD drives. Currently, the fastest standard is SATA III with a bandwidth of 6 Gbit / s.
The M.2 connector is a new standard that is used to connect SSDs in this format. It should be noted which bus this port works with. It can be both SATA III and PCIe – of course, the latter guarantees much higher performance. Additional acceleration will also be provided by the support of the NVMe protocol. There are also different sizes of such disks, but most motherboards are prepared for this.
Another thing to note is the ports on the front panel. Apart from the connectors for turning on and restarting the computer, of course, there are USB or audio ports on the panel. It is therefore worth checking if the board has a sufficient number of, for example, USB 3.0 connectors.
Fan connectors on your motherboard will be especially useful if you don’t have a fan speed controller. One of them is always dedicated to CPU cooling (usually signed CPU_FAN). You can also meet a water pump connector – it will come in handy when you use water cooling.
Other connectors that you can find on the MOBO are, for example, the connector for LED strips and the U.2 port.
LED RGB / ARGB connectors. If you care about housing with fans, RGB stripes, it is worth synchronizing the whole thing. In order to control these lighting systems, they must be connected to a compatible RGB or ARGB connector. The difference in these standards is the number and layout of the connection port pins. As standard, it is 4 pins for RGB and 3 pins for ARGB in a 1–2 system. In addition, the selection of the appropriate standard is important because no adapter can be used here. RGB fans have the ability to control a uniform backlight color, while the ARGB standard has individual LEDs, which gives a much wider range of control, and thus many options for illumination effects.
Integrated sound card
Today, every motherboard has its own audio chip. If you are not an audiophile, but you want reasonably good sound quality – pay attention to the card implemented by the MOBO manufacturer. If the sound is not that important to you, or you simply reach for an external sound card, the integrated circuit does not play too much of a role when choosing a disc.
Currently, Realtek chips are the most popular. There are several models available, and below we have ranked them from the best quality: ALC 1220, ALC 1150, ALC 982, and ALC 887.
Before choosing, it is also good to check whether the sound system has been separated, i.e. whether it has separate layers on the PCB laminate. This solution increases the cost of production, so it is mainly found in more expensive motherboard models, but it allows to reduce signal distortions and noise. Manufacturers often emphasize this by separating the audio circuit with an LED backlight.
Additional modules
Motherboards can be equipped with additional modules such as Wi-Fi or Bluetooth. If you plan to use such a solution, instead of buying additional accessories, look for a model equipped with the appropriate system.
Manufacturers technologies
Often motherboards, apart from basic components and functions, offer something extra. Manufacturers use different nomenclature for, as a rule, the same functions.
- Reinforced structure – most often you can find boards that are made of more durable materials, PCIe connectors have additional reinforcements, and the slots are abrasion-resistant.
- Overclocking Support – Some boards come with preset overclocking settings. Just select the appropriate option in UEFI and the MOBO will automatically adjust the CPU clocks and voltage. However, caution is advised when using these tools. They often boost the CPU voltage very high, causing it to overheat unnecessarily, thus increasing the noise generated by the cooling system.
- Improving the sound quality – this is one of the most used add-ons.
- Support for network connectivity – these are techniques that are to improve the quality of the connection and reduce interference and delay.
These are, of course, only a few of them. The list of technologies used by manufacturers is very long.
Motherboard and CPU overclocking
If you plan to overclock your processor, apart from choosing the right chipset, you should also pay attention to several other aspects, such as the power section or DualBIOS.
CPU power section
When overclocking the processor, its power section is extremely important. The better, more powerful the section, the more stable the processor will be. In this case, attention must be paid to the number and quality of chokes and capacitors on the motherboard, as well as the MOSFET. However, the easiest way is to simply browse the internet in search of reviews and opinions about a given board or pay attention to the photos of the motherboard and verify how complex the elements above and to the left of the processor socket are.
If you plan on overclocking, or buy a 6-core processor or more, opt for a board with a cooled section. It will allow you to maintain higher CPU clocks during prolonged load of the unit.
BIOS and DualBIOS
Let’s start with what a BIOS is. It is the Basic Input / Output System, i.e. the basic input / output system. Controls data transfer between components. As soon as the computer starts up, it also performs a series of component tests, and informs the user of any errors with beeps, on the computer screen or on the POST code display. This is where, for example, the procedure of overclocking the processor or RAM is performed.
So what is DualBIOS? Nothing but two such systems. This is useful when the primary, default BIOS crashes. You can then easily restore it with the second system.
What gaming motherboard?
Wondering which gaming motherboard will work best? You don’t have to invest a huge amount of money to buy a gaming unit. However, there are some features that should be taken into account when buying this type of model, such as improved audio parameters with available noise reduction or a strengthened PCIe x16 slot. In addition, you can verify the necessary slots dedicated to intense entertainment, for example, USB or PS2. In addition, overvoltage protection is useful – thanks to it you will avoid the risk of overheating and failure.
Differences between cheap and expensive gaming motherboards
More expensive motherboards
Professional players are among the most demanding customers, so they expect top-shelf equipment. Top models offer the richest set of connectors, which will allow you to build extensive sets, not only for gaming but also for video processing or streaming gameplay.
These customers also often choose to overclock components, which translates into even better performance. So we can expect an extensive, efficient power section and additional functions to help speed up the computer. Unfortunately, the top albums are also correspondingly more expensive.
- large set of connectors
- extensive and efficient power section
- additional functions to help speed up the computer
Lower-end motherboards
Manufacturers are also increasingly noticing hobby players who have different requirements and want to spend a smaller budget on the purchase of a gaming motherboard. In this case, the set of connectors is usually limited to the bare minimum – it allows you to put together a good kit for everyday gaming.
We will not always find a better network or sound card. All this means that cheap gaming motherboards are basically distinguished only by a more effective design compared to standard models.
- minimum set of connectors
- weaker video and sound card
What is the price to buy a motherboard?
A good Intel motherboard or AMD motherboard doesn’t have to be expensive to do its job. If you do not need additional slots or functions to configure, such as RGB backlighting, you can buy a component at an affordable price and it will certainly serve reliably in the basic application. The optimal solution is to choose a medium-price plate that guarantees adequate performance and smooth operation of the entire unit.
Conclusion
When choosing a motherboard, it is worth considering its purpose, the number of ports, and connectors. It is also crucial to match the chipset to the operational parameters and type of the processor as well as the types of supported technologies.
Expensive motherboards are designed for more advanced tasks. With extended systems in mind, it is worth considering, among others: OC type socket, guard-pro (which is designed to protect the equipment from overload), TUF components (providing reinforced materials from which the equipment was created), and the Ethernet killer (with a fast port LAN).




